特點(diǎn)與優(yōu)勢(shì)


ScintiStar detectors use a rare-earth-based ceramic material with a cubic garnet crystal structure, resulting in greater X-ray sensitivity, a 150-fold increase in visible light conversion rate over GOS, and reduced afterglow. It allows for more data to be acquired every rotation while generating less electronic noise, resulting in high-resolution images.
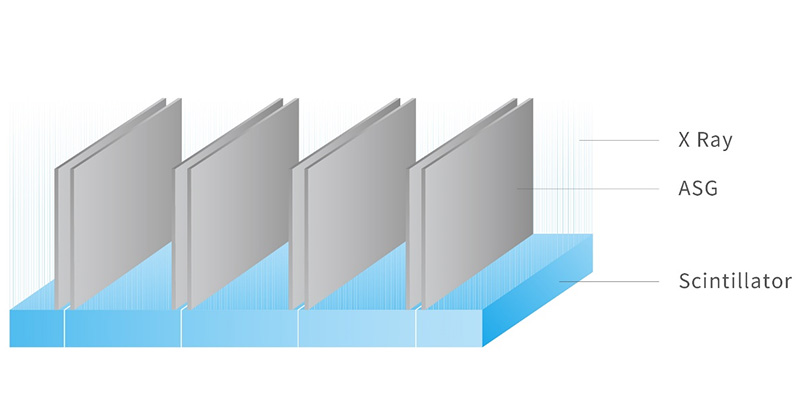
Due to its ability to effectively absorb the scattering X-ray, the anti-scattering grid (ASG) plays an important role in detector sampling. Unlike standard ASG designs, which use the same grid for neighboring modules, MinFound EAA ASG uses a separate grid between adjacent modules, considerably minimizing the possibility of grid expansion due to heat, and thus reducing the presence of artifacts in images.

The ScintiStar detector masterfully incorporates an ASG, a scintillator array, a photodiode, and an ASIC chip into a small module. This architecture improves the signal-to-noise ratio while also allowing for more modularized maintenance.